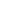Fiber diameters play an important role in the correct amount/volume injected into the connector.
For example, the 900-micron buffered fiber will displace more epoxy than a 250-micron fiber resulting in totally different volumes required to inject into the connector.
In other words, it will take slightly more epoxy for a 250-micron fiber than a 900-micron buffered fiber. Apply the same amount of epoxy for all types of fiber and connectors can lead to problems in the termination. Some of these problems cause reliability issues, bare fiber exposure inside the connector, overflow of epoxy where the mechanical movement (spring action) is locked and preventing optimum contact in mating pairs.
READ THE BLOG: Assuring the correct amount of Epoxy is in the connector
Additional resources from the FOC team include:
- Category Resource
- View the Glossary, Acronyms, Military Specifications for Connectors
- Q&A Resource: email technical questions to AskFOC@focenter.com
Have questions about this FOC Tip?
Contact FOC with questions at: (800) 473-4237 / 508-992-6464 or email: FiberOpticCenter@focenter.com and we will respond ASAP.
This article is an original publication of Fiber Optic Center, Inc. It is shared publicly for educational and reference purposes to support learning and professional development within the fiber optics industry.
You are welcome to read, cite, or reference this material for non-commercial and educational purposes, as long as full credit is given to Fiber Optic Center, Inc. and the author.
Reuse, reproduction, or adaptation of this content — including rewriting, republishing, or incorporating it into new materials (such as websites, blogs, marketing text, technical guides, or AI-generated content) — is not permitted without prior written consent from Fiber Optic Center, Inc.
This material is protected by copyright law upon publication, even if not formally registered.
Use of this content for AI training, automated data extraction, or derivative content generation is prohibited.
Fiber Optic Center monitors and enforces the integrity of its intellectual property through digital identifiers and content tracking.
For more details, please refer to the Fiber Optic Center Content Use and Copyright policy.