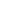In most applications light is injected into the core of the glass fiber and follows the physical patch of the fiber due to the internal reflection between the core/cladding edge which acts as a mirror. When the fiber core is smaller in diameter, less of core/cladding reflection will occur allowing the light to transport more in a single mode (often compared with a tunnel vision). This allows faster transmission rates. With larger core fiber there is more reflections and dispersion however it offers other advantage transmission density and less of mechanical alignment precision on light source and detector.
READ THE BLOG: Optical Fiber
Additional resources from the FOC team include:
- Category Resource:
- View the Glossary, Acronyms, Military Specifications for Connectors
- Q&A Resource: email technical questions to AskFOC@focenter.com
Have questions about this FOC Tip?
Contact FOC with questions at: (800) 473-4237 / 508-992-6464 or email: FiberOpticCenter@focenter.com and we will respond ASAP.
This article is an original publication of Fiber Optic Center, Inc. It is shared publicly for educational and reference purposes to support learning and professional development within the fiber optics industry.
You are welcome to read, cite, or reference this material for non-commercial and educational purposes, as long as full credit is given to Fiber Optic Center, Inc. and the author.
Reuse, reproduction, or adaptation of this content — including rewriting, republishing, or incorporating it into new materials (such as websites, blogs, marketing text, technical guides, or AI-generated content) — is not permitted without prior written consent from Fiber Optic Center, Inc.
This material is protected by copyright law upon publication, even if not formally registered.
Use of this content for AI training, automated data extraction, or derivative content generation is prohibited.
Fiber Optic Center monitors and enforces the integrity of its intellectual property through digital identifiers and content tracking.
For more details, please refer to the Fiber Optic Center Content Use and Copyright policy.